Browsing experience has always been about clicking links, reading articles, and maybe interacting with ads. But imagine a browser that doesn’t wait for the clicks because it can think, plan, and act on the user’s behalf, i.e., an agentic browser.
Agentic Browsers are powered by autonomous AI agents that can answer users’ queries using active automation. While traditional browsers are passive displays of user queries, agentic browsers act as proactive collaborators and work towards providing an answer rather than resources.
Since this will lead to a change in primary consumers of content from users to AI agents, the old metrics of engagement, i.e., page views, ad impressions, and time-on-site, will not remain relevant. Therefore, publishers need to restructure their action plan on the basis of how they can be relevant to AI and algorithms.
Let’s take a deep dive into the world of agentic browsers; what they are, why they matter, and how they’re shaking up the publishing landscape in the coming future.
Key Takeaways
- Agentic Browsers merge automation and intelligence by combining AI reasoning with browser functionality. They analyze, plan, and execute complex workflows all in real-time.
- Websites now need to serve two audiences: humans and AI agents. This means cleaner structures, semantic HTML, and API-first architecture.
- Structured content is becoming a sellable asset. Publishers are now exploring premium APIs and machine-readable licensing to monetize data directly for agentic browsers.
- Industry analysts predict it will reach $140.8 billion by 2032, signalling a massive shift in how we interact with and monetize the web.
- With AI agents controlling browsing, data permissions, trust, and security models need complete redesigns.
What are Agentic Browsers Exactly?
Think of a browser that doesn’t just show web pages but understands what the user wants to achieve. It reasons through users’ goals, plans next steps, and completes actions for them. That’s what makes an agentic browser different. Rather than relying on manual clicks and navigation, it leverages large language models (LLMs), APIs, and user intent modelling to function as a goal-oriented decision engine.
In this setup, users are not searching or filling out forms; they are simply expressing what they want.
In simple words, an agentic browser processes user intent, executes tasks, and adapts as it learns. It’s like having an intelligent co-pilot that can research, summarize, fill forms, and interact across websites. This marks a major shift in how users experience the web, making it a new way to browse the internet.
Use Cases and Benefits
Here’s a quick overview of how users can use agentic browsers:
- Users can summarize long blog posts, PDFs, and research papers
- Auto-fill CRM records and online forms.
- It can be used to track product prices across multiple sites.
- Collect and compile competitor data into reports.
- Use it to book meetings and send follow-up emails.
By combining automation with intelligence, they offer a range of benefits that go far beyond convenience:
- Save Time on Repetitive Tasks: Agentic browsers handle multi-step workflows in seconds, freeing up hours each week for the user.
- Boost Productivity and Focus: By offloading routine chores, users can concentrate on strategic thinking, bring creativity to their work, and make decisions.
- Smarter Information Consumption: Agentic browsers deliver distilled insights as per users’ needs.
- Personalized Automation: These tools adapt to users’ preferences, learning how they work and customizing their actions for better results.
Quick Recap: Agentic browsers don’t show search results; instead, they understand what the user wants, interact with pages, and complete the query in an answer format.
How Do Agentic Browsers Work?
Agentic browsers adapt to different site designs, handle unexpected changes, and learn from experience to get better over time. They treat every website as a programmable interface, turning users’ instructions into real-world actions while users focus on higher-value work.
Here’s how they do it:
Step 1: Understand Users’ Intent
Firstly, the AI agent analyze the user’s request. It breaks down the goal into smaller, actionable tasks.
Step 2: Analyze Websites for Data
Second, the webpage is scanned to understand its structure and find relevant information.
Step 3: Plan the Actions
Using the user’s intent and the site’s layout, the agent builds a plan. This may include:
- Navigating references through multiple pages
- Filling out forms with relevant information
- Comparing options across different sections for more precise information.
Step 4: Execute and Adapt
The second last step includes the agent performing the planned actions while monitoring for issues. If something doesn’t work, it adjusts in real time to keep the task on track.
Step 5: Validate the Outcome
Once the task is complete, the agent checks if the goal was achieved. It can:
- Confirm a successful booking or purchase
- Detect if further steps are needed
- Provide a summary of what was done
Quick Recap: Agentic Browsers execute tasks, adapt to changes, and validate outcomes like bookings or purchases by treating websites as a source of information. They can also automate workflows and improve over time, saving users’ effort and boosting productivity.
Role of Agentic Browsers for the Web Ecosystems
The silent shift of web ecosystems is transforming how websites are built, optimized, and monetized in 2025. Agentic browsers are a new kind of browser that interpret user goals and execute tasks autonomously. They treat websites not as visual experiences but as functional systems. This shift forces designers and publishers to rethink how content is presented, built, and measured.
Design for Two Audiences: Humans and AI Agents
Web interfaces are no longer just for human eyes. Developers and publishers must now consider how AI agents interpret and interact with content. This means:
- Create clean navigation structures
- Reduce dependence on JavaScript elements
- Increase in the use of well-structured layouts and HTML
The Rise of API-First
While visual design still matters for human engagement, websites will increasingly need to expose their data and functionality through APIs. This dual-layer approach will allow visuals for human engagement and programmatic engagement for agents.
UX and SEO Centric Web Design
In the past, publishers focused on making content crawlable and keyword-rich for search engines. But agentic browsers don’t just crawl; they evaluate websites based on three questions:
- Is the content enough to complete the task?
- Is the information structured and reliable?
- How quickly can the agent reach the goal?
If a website prioritizes these factors, it will gain a competitive edge in this changing environment.
Publisher and Monetization with Agentic Browser
After this trend caught speed, publishers are trying to find ways to earn revenue with their structured content, since without human impressions, ad revenue will no longer be in the picture when it comes to agentic browsers. Here are some strategies to treat structured content as a product in itself.
- Offering premium APIs allows agentic browsers and AI agents to access high-quality, structured data directly from the source.
- Licensing content for machine-readable consumption, particularly in data-rich sectors like finance, healthcare, and academic research, where accuracy and freshness are critical.
- Subscriptions & Memberships: Offer premium content, ad-free experiences, or exclusive perks that deepen audience loyalty and generate predictable recurring revenue.
- Sponsored Content & Partnerships: Collaborate with brands to produce high-quality, relevant content that delivers value to readers while unlocking premium revenue opportunities.
What Publishers Can Do to Stay Resilient?
By offering flexibility, scalability, and real-time optimization you can maintain consistent revenue and better fill rates, even during changing trends.
You can tap into Direct Deals to gain control over pricing, targeting, and campaign pacing.
Deliver ad experiences that align with diverse campaign goals and budgets. By focusing on UX-focused ad performance and expert AdOps support, you can stay optimized without added workload.
Use first-party data to build high-value audience segments to offer advertisers smarter targeting and higher engagement.
Quick Recap: Websites are now built for both humans and AI agents, with clean layouts and API access. SEO practices might shift from keyword focus to task efficiency. Also, publishers will monetize structured content through premium APIs and license it in the future.
4 Leading Agentic Browser Platforms in 2025
Many companies are leading a transformation to agentic browsers, in the hope of bringing unique capabilities and challenges to the table:
1. OpenAI Operator
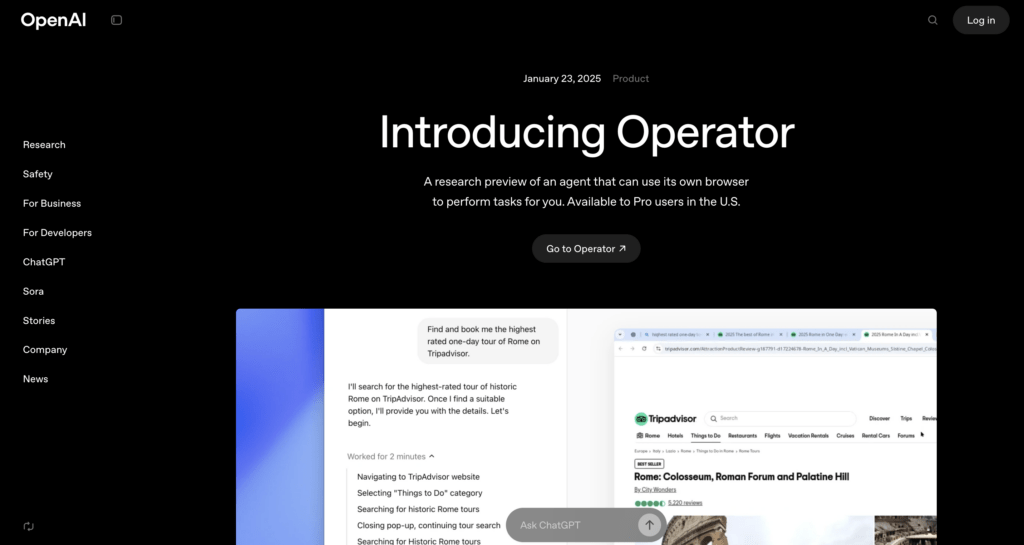
It enables autonomous tasks execution like research, summarization, and navigation. OpenAI’s operator integrates with browser actions, enhancing productivity but raising concerns about permission control and agent misuse of sensitive data.
2. Google’s Project Mariner

Project Mariner integrates Gemini AI into Chrome for multi-tab control, contextual editing, and AI-powered suggestions. The main aim is to streamline workflows. It also introduces enterprise risks related to data privacy and AI-driven command execution.
3. Opera Neon

It focuses on AI agents for content generation and multimedia manipulation. Opera Neon reduces latency and enhances privacy, but may expose systems to risks from unmanaged local agent behaviour.
4. Fellou & Nanobrowser
It is designed for automating complex workflows like form-filling and multi-site summarization. Fellou & Nanobrowser increase productivity for publishers and power users but share risks with bot frameworks, including potential misuse for unauthorized access.
Security, Privacy & Trust Considerations
Agentic Browsers are a calculated move by leading AI and model companies responding to a convergence of strategic imperatives. These browsers are becoming the new frontier for AI deployment, and here’s why:
Interfere Control
Browsers are the most-used application in enterprise environments, serving as the gateway to user behaviour, workflows, and data. By building their own browsers, AI companies gain full control over how users interact with their models.
Building a Defensive Moat
Embedding agents within proprietary browsers protects against platform-level disruptions. If mainstream browsers restrict AI agents or limit automation, owning the browser ensures continuity, resilience, and strategic independence.
New Operating System
Agentic browsers are shifting user attention away from traditional apps and toward prompt-driven workflows. They are redefining the browser as a command center for executing tasks are execution through intent.
Market and Behavioural Shifts
Industry forecasts have projected that the agentic AI market will reach $140.8 billion by 2032. Meanwhile, the rise of “zero-click” searches signals a broader shift toward AI and away from conventional navigation.
Vertical Integration for Speed
Companies like OpenAI (with Operator) and Google (via Project Mariner) are embedding their AI directly into the browser layer. This will improve responsiveness and create a seamless feedback loop between user actions and model behaviour.
Quick Recap: By 2032, the agentic AI market is projected to reach $104.8 billion. Agentic browsers shift by embedding AI into browsers for speed, resilience, and user insight, marking a major shift in how we use the internet.
Ask ChatGPT This:
Try this — a quick ChatGPT question to explore the topic further.
Frequently Asked Questions
Seraphic’s browser agent is super, where AI agents autonomously navigate and execute tasks online. As browsers evolve into intelligent interfaces, Seraphic provides real-time protection against threats like unauthorized automation, malicious scripts, and data leakage.
Agentic Browsers are intelligent assistants rather than passive tools. While traditional browsers rely on clicks, scrolling, and interpreting content, agentic browsers understand user intent and execute tasks like booking reservations or summarizing articles without any manual input. They treat websites as functional systems, navigating forms, buttons, and menus programmatically.
The first agentic AI browser is widely recognized to be Fellou, which launched as “the world’s first agentic browser”. Fellou was designed to enable autonomous task execution, such as multi-source research, form-filling, and workflow automation, based on natural language commands.