Publishers with video ads enjoy the best average CTR out of all digital ad formats, approximated at 1.84%.
Hence, video advertising has made a compelling case for itself in the last 5 years. As per a report published by eMarketer, video advertising accounted for half of the programmatic spend in the year 2019. And with the introduction of outstream video ads, leveraging this format for revenue growth has become easier.
In any case, publishers must start experimenting with video ads in order to earn more revenue. In this post, we cover how to start with video ads in Google Ad Manager.
Video Ad Types Supported in Google Ad Manager
Before beginning with the process of running video ads in GAM, publishers must first have an understanding of the ad types that Ad Manager supports. GAM allows three types of video ad types: Linear, Non-linear, and Companion.
Linear
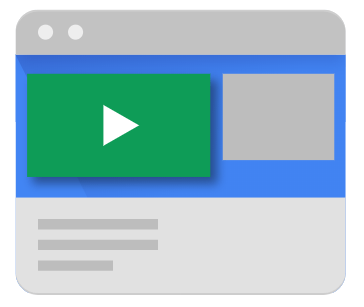
Linear ads are only played with the help of a video player. They are a form of in-stream ads and are of three types:
- Pre-roll: These ads are played in the beginning of the video.
- Mid-roll: These ads are played in-between the video content
- Post-roll: These are played after a video ends.
Non-linear Ads
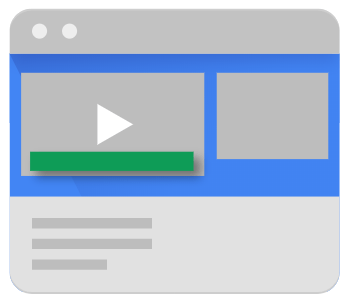
These are also in-stream video ads but they do not disrupt the playback. For example: banner ads that appear at the bottom of YouTube videos. A good practice is to include these ads in the top or the lower 1/3rd of the video. They can be either display or video-based ads and are of two types: overlay and non-overlay ads.
Companion Ads
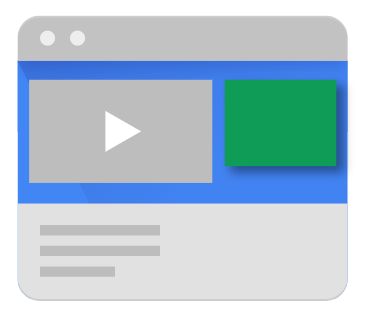
Companion ads are placed around the video player on the webpage where the video is being played. These ads allow you to link non-video ad units to video player on the same webpage. They also depend on master video to serve. They are either text or image based and help publishers get additional revenue without letting users get distracted.
Pre-requisites of running video ads in Google Ad Manager
Before we proceed with understanding how video ads are run in Google Ad Manager, we must first look into some of the necessary conditions for setting up these ads.
- Video Players: In order to run video content (including ads) on a website, publishers need a video player. While there are multiple options available, Google offers their own list of partners to get started with.
- Although optional, but highly recommended is the integration of the video player with Google IMA SDK. This is beneficial for all publishers as the IMA SDK supports all video templates by IAB: VAST, VPAID, and VMAP.
How to Run Video Ads in Google Ad Manager?
The process of implementing video ads in Google Ad Manager is a 5-step process:
- Step 1: Create Ad Units
Ad units are the spaces on a publisher’s inventory where they want to display ads. The first step to running these ads is creating ad units to run ads on. Here’s how you can do it:
Sign in to your Google Ad Manager account.
Click on Inventory >> Ad Units.
You need to select a hierarchy level for the ad unit. This can be done by either selecting a parent ad unit or the ad unit will run at the top.
Click on New ad unit.
Now enter a Code. This will help in identifying the ad unit in the associated ad tag. For example, mysite_economy_home.
Provide a Name and Description for the ad unit.
Select a size for the ad unit. You can select two sizes: Fixed and Smart.
In case you are using Video Solutions offered by GAM, the next step is to enter the default master video and companion slot sizes. Master video size is the size of the video player in its most favoured aspect ratio.
Select Target window which has two options: Top and Blank. Target window is important as it defines the window in which the landing page will open.
Set Frequency Caps which defines the number of times a user will see the ad on their screen.
Click on Save. - Step 2: Video Ad Tag Generation
Once you have created the ad unit, the next step is to generate ad tags. Ad tags are important because they contain all kinds of information required in a video ad request. This can include anything related to the companion ads or the master video ad.
Here’s how you can generate ad tags for the video ad units:
Click on Inventory >> Ad Units
Select an existing ad unit and click on Tags.
Select the Tag Type. Most common is the Google Publisher Tag.
Select the SDK type. If you do not have an SDK, opt for no SDK. In most cases, a publisher is using the Google IMA SDK, so select that.
You can then add optional parameters in the tag.
Copy the generated ad tag. - Step 3: Creating Video Line Items
Once you’re done with generating a video ad tag, the next step is to create a line item. But before that, defining orders is mandatory. Once that’s done, here’s how you can proceed with line item creation;
In your insertion order, click on the New Line Item button.
Click on Video.
Assign a name to your line item.
The next step is line item targeting. For these ads, there are four kinds of targeting available: Content targeting, Position targeting, Request format targeting, and Request platform targeting.
We’ll cover the three major kinds of targeting: Content, Position, and Request Platform Targeting.
Content Targeting: Through this, publishers can monetize video content more efficiently by targeting ads to that specific content. This is done by collecting metadata by connecting your Content Management System to Google Ad Manager. Here’s how you can do this;
Click on Video >> Content Sources >> New Source.
Enter a source name, after which you will need to select a Content Type.
Choose one of the three available type options: MRSS Feed, Ooyala, Brightcove. Each type requires individual credentials. For example, for Ooyala, you will need to enter API key and API secret.
Next step is to select a sync rule which is of two types: Automatic and Manual.
Click on Save.
Position Targeting: Through this, publishers can target video line items to specific video positions such as pre-roll, mid-roll, etc. But for this, the first step is to set ad rules. This helps in setting parameters such as how long the ad will be played and others. Here’s how you can do it:
Sign in to your Google Ad Manager account.
Click on Video >> Ad Rules >> New Ad Rule.
Pick and enter a name for the rule, followed by selecting the status, and either of the two ad rule types: Standard and Session. Configuration of either of the rules is a lengthy process and requires a thorough understanding of settings.
Next step is to choose schedule time for the rules. Select Unlimited if you want the ad rule to run indefinitely.
Click on Targeting to match the ad rule with specific ad requests.
Click on Save.
Request Platform Targeting: Publishers can use this to target video line items to specific ad request platforms. Here’s how you can do this:
Sign in to your Google Ad Manager account.
Select a video line item or create a new one. And then click on Settings.
Under the Add Targeting section, click on Inventory Type. Select any of the available inventory types including In-stream video, App display and out-stream, Web display and out-stream.
Click on Save. - Step 4: Adding Creatives to Line Items
Video line items require addition of creative sets into them. Here’s how you can do it:
Click on Delivery >> Line items.
Select and open your video line item.
Click on Creative >> Add Creative >> New Creative.
You will then need to select a VAST creative. Ad Manager supports four kinds of VAST creatives: video, overlay, redirect, and set-top box.
Configure settings according to your preferences and click on Save. - Step 5: Creating Reports
Reporting for video ads in Google Ad Manager works exactly the same for any other ad format. Here’s an extensive guide on how to generate reports in GAM.
Conclusion
Understanding the process of running video ads in Google Ad Manager can get tricky in the beginning and publishers may face technical difficulties. But the growth that video advertising will bring to your revenue is worth the effort. In case doing this on your own is too difficult, we have created a list of video ad networks that can help you achieve this.
FAQs
With Google Ads, you can promote your business, sell products or services, raise awareness, and increase website traffic. Using Google Ads, you can create and modify your ad campaign online, including ad text, settings, and budget.
The cost per click for Google Ads Search is $2.32. The cost per click for Google Ads Display is $0.67. The cost per click for Google Ads Shopping is $0.54 per click. The cost of Google Ads Video is $0.1 per view.
In Google Ads, you pay for each click (PPC). It means marketers bid on a specific keyword on Google and compete with others who are also targeting the keyword. Your bids are “maximum bids” – the maximum you’re willing to pay.

Shubham is a digital marketer with rich experience working in the advertisement technology industry. He has vast experience in the programmatic industry, driving business strategy and scaling functions including but not limited to growth and marketing, Operations, process optimization, and Sales.