The popularity of video ads is undeniable, and in the coming years, video ads will become a driving force of digital advertising. Here is an overview of the Types of Video Ads, best practices, and how video ads are served.
Video brings more viewability to your ads. Since users prefer video ads, marketers and advertisers are investing more in them.
Thanks to technological advancements, advertisers have all the right tools and software at their disposal to create video ads and launch video ad campaigns. There are types of video ads and formats that publishers should know, their advantages, and use cases where these formats best apply.

- According to the Statista report, ad spending in the Video Advertising segment is projected to reach US$210.20bn in 2023.
- In the Video Advertising segment, US$250.10bn of total ad spending will be generated through mobile in 2027.
- Connected TV is expected to show an annual growth rate (CAGR 2023-2027) of 11.72%, resulting in a projected market volume of US$48.63bn by 2027.
Looking at the growth of video advertising, we created this guide to help publishers get started with video advertising and video ad types.
Also Read: 7 Video Ads Best Practices to Follow in 2023
I. What is Video Advertising?
As the name suggests, video ads are short videos containing a brand’s message to its users. Initially, only publishers with video content (like YouTube creators) used this method to monetize their traffic. And they still do.
Looking at the better engagement rate, editorial publishers started investing their time in video ads. Programmatic advertising enabled publishers to target, manage, and scale video advertising strategy just like their display ads.
Video Ads are Served by Four Mediums, these are:
- Social media (Facebook, Instagram)
- In-App Video Ads
- OTT (Over-the-Top) Devices
- CTV (Connected TV)
- Web-based Video Ads (desktop and mobile)
Video advertising allows you to engage with audiences that ignore banner ads or text. A lot of marketers are increasing ad revenue by investing in video ads. If you overlook this trend, you’ll face a competitive disadvantage.
II. What Are the Types of Video Ads?
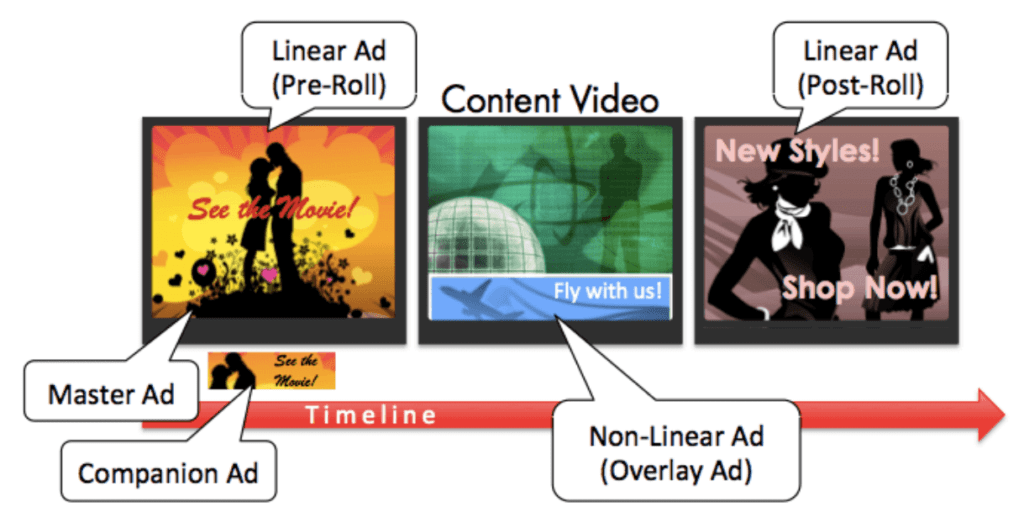
This article describes the types of video ads and formats available for publishers. Digital video ads can be split into two formats – linear and non-linear. Explore the points in detail below.
Linear Video Ad Format
Linear video ads can be displayed between streaming video content or a TV commercial.
This ad format is relevant to the context, and use cases, from sports and beauty brands to entertainment, edtech, and fintech linear video ad format is the preferred choice of marketers. The Linear Ad Format can be categorized into pre-roll, mid-roll, and post-roll ads.
Non-Linear Video Ad Format
These ads run along with the video content without any interruption. Clicking non-linear ads pause the video content. These ads redirect the user to your website when these ads are clicked. These ads are categorised into overlay and non-overlay ads.
Non-linear video ads also fit most of the business verticals because of their unobtrusive nature, which makes them perfect for live streams of events.
Companion Ad Format
Companion ads have the features of both linear and non-linear ads. These ads come in different sizes and in the form of text, static image display ads, or rich media. These ads offer an interrupted video streaming experience.
Also Check: IABs Video Ad Standards: Everything You Need to Know
The video ad types can be split into in-stream & out-stream ad units.
1) In-Stream Video Ads (Linear Ad Format)
In-Stream video ads are played before (pre-roll), during (mid-roll), or after (post-roll) the streaming video content. The types of In-stream video ads are displayed within the context of streaming video. Pre-, mid-, and post-roll video ads are linear ad formats that appear before, within the break, and after the video content plays, respectively.
The Pre-roll ad type is perfect for building brand awareness.
Here are the types of pre-roll ads:
- Bumper Pre-Roll Ads – These ads play before the main video content. The ad can be up to 6 seconds in length.
- Non-Skippable Ad – These ads can play before, during, or after a main video. It can be between 15-20 seconds in length.
- Skippable Ad – These ads can also play before, during, or after a main video. The length of the video can be of several minutes, but viewers can skip the ad after 5 seconds.
Mid-roll ads are great for enhancing user experience.
- The maximum length of mid-roll ads depends mainly on the platform. For example, if you’re posting your mid-roll ad on a YouTube video which is 10 minutes long, the ad can be anywhere between 5 and 30 seconds.
- On Facebook, if your video is between three to four minutes, the ad length will be between 10 to 15 seconds.
Post-roll ads add more value to your campaign with a clear and concise call to action.
- This ad type only appears on videos that have opted for the ad revenue program.
- These ads are typically 10 to 15 seconds long and can also be as long as three to four minutes.
- Notice the yellow line at the end of the video. This indicates a post-roll ad will play.
- For ads that include a call-to-action (CTA), the post-roll ad is likely a good choice.
- For example, Nike or Adidas might use a post-roll advertisement to promote their newest range of sports & fitness accessories with a CTA that directs the viewer to the product page to make a purchase.
2) Outstream Video Ads
The outstream video ad allows publishers to show video ads irrespective of video or non-video content. Meaning publishers with editorial content can show ads in video format and monetize with better engagement promised by these.
Outstream video ads are placed outside of the in-stream video content. This ad type appears not along with the video content but in the standard display ad units on the webpage.
Publishers can leverage out-stream video ad types to increase brand awareness, drive online purchases, target key consumers, and extend ad campaign reach.
Noticed autoplay ads on Forbes pages? Those are examples of out-stream ads.
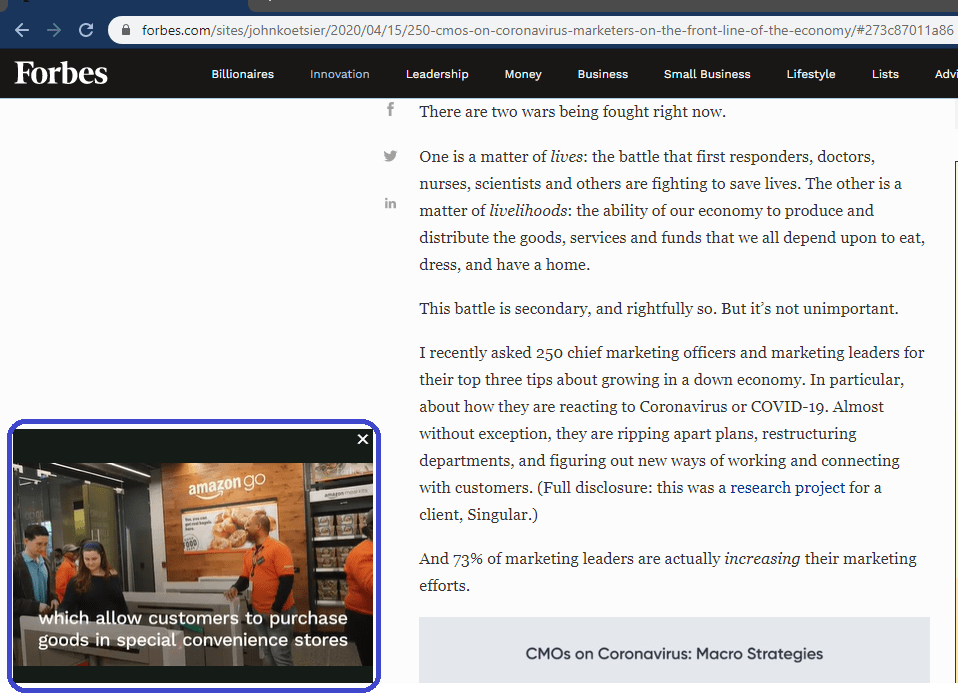
Outstream video ads can further be classified as:
- In-Page Ads: Use a dedicated video player to show video ads within content.
- In-Banner Ads: Update the existing ad units (dedicated to the banner) to show video ads as well.
- In-Text Ads: Designed to appear after a certain user engagement, click 50% scroll and hover over a specific part of the page.
3) Overlay Ads (Non-Linear Ad Format)
Overlay ads run on top of the video and cover only 10-20% bottom part of the video content to avoid obstruction. These ads are used to showcase a brand or product while the video content is played. But these ads could cover important information like subtitles or captions in the video.
4) Non-Overlay Ads (Non-Linear Ad Format)
Non-Overlay ads run along with the video content instead of overlaying it. You can use these ads to interact with the video content. The best part is that video content is not at all obstructed.
5) Interactive Video Ads
You might have noticed this ad type on mobile game apps, a short video appearing after you complete a level. Interactive video ads launch after a certain activity completed by the user – it can be completing a level, clicking on a certain part, or hovering over it.
Publishers with low bounce rates also place these interactive ads on desktop and mobile websites.
As these ads generally appear only after certain user interactions, they tend to offer better engagement. It is best to keep the ad length limited to 20 to 30s only.
Also Read: How to Boost Your Video Ad Revenue: A Checklist for Publishers
III. What Platforms are Needed For Serving Video Ads?
Just like display ads, there are tons of platforms involved in the case of ads in video format. Here are some important ones:
Video Ad Networks
These platforms facilitate the exchange of a part of (video) inventory allowed to them by publishers, SSPs, or ad exchanges. Then they connect to high-paying quality advertisers or DSPs, present them with the inventory and sell for a higher price. Before choosing a video ad network, evaluate its revenue models, reporting, and traffic requirements.
Video SSPs and Exchanges
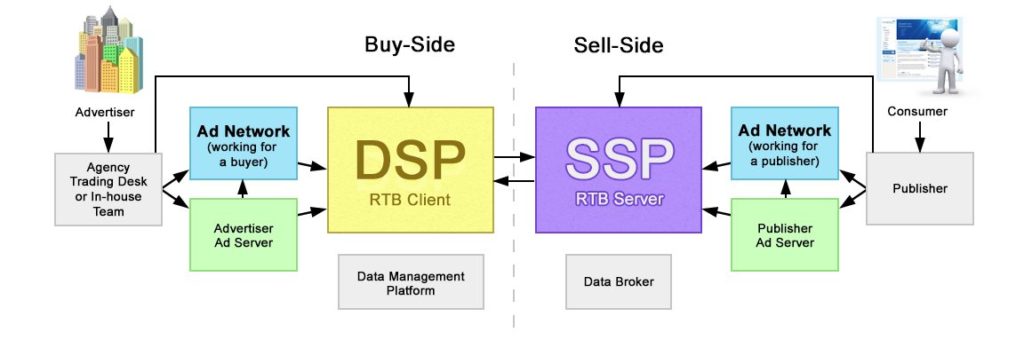
Video SSPs are marketplaces for video ads. Advertisers and DSPs looking for video inventory can find them here, segmented by targeting options. Their services include analytics and reporting, yield management and optimization, and inventory management. The names of a few popular ones are Xandr, Verizon Media, SpringServe, SpotX, and Teads.
Video Ad Servers
Once an auction is concluded or a deal is made, the video ad server puts the ad onto the webpage. It acts as a centralized storage system for all ad creatives and takes care of timely delivery. Names of a few video ad servers are – Google Ad Manager, SpringServe, and Epom.
Video DSPs
These are advertisers’ side platforms used to set the right campaign for their brands. DSPs help advertisers with targeting, finding the right audience, helping them set their bidding model, and finally, sharing their creatives with ad servers.
IV. What Are the Technologies Involved in Video Ads?
Video advertising is always considered more complex than display advertising. Additionally, video ads need a video player to run. This is why, earlier, only video content providers were running video ads. They had a video player in place already, they just needed interested advertisers, and then they could easily patch advertisers’ videos with their own video content.
Ad tech was facing two issues when it came to showing video ads with editorial content—serving format and player.
These were solved by a technology called:
- VAST or Video Ad Serving Template.
IAB introduced VAST, and the recent version in use is VAST 4.2. Before this, the industry was investing in VPAID (Video Player Ad-serving Interface Definition), another technology by IAB released in 2012.
VAST 4.2 controls the delivery of video ads and also help determines the various assets of the ad, such as– media files, verification scripts and interactive scripts. OMID is used to measure viewability, and SIMID controls interactivity.
VPAID offered limited transparency and created various issues in the industry associated with trust, vulnerabilities, negative user experiences and poor fill rates. Hence, the adoption of video ads was low.
However, VAST and VPAID are both being used in the industry right now, as many brands are still working on shifting from VPAID to VAST. Google uses the latest version of VAST for video ad serving via Google Ad Manager.
The introduction of VAST 4.2 also means the final killing-off of VPAID, a format that wasn’t originally met with good reception and may have been the reason for the slow adoption of a common schema.
VPAID offered limited transparency and created various issues in the industry associated with trust, vulnerabilities, negative user experiences and poor fill rates.
Read More: VAST vs VPAID: What They Are, How They Work, Differences [+ More]
V. How Are Video Ads Served on a Website?
Video ad serving is pretty much the same as display ad serving with the addition of steps related to VAST signal exchange. Here are the exact steps:
Step 1. A user appears on the publisher’s website with a video ad unit.
Step 2. The ad tag (VAST code) inside the ad unit sends a signal to get a video for the impression.
Step 3. The signal is passed to connected ad networks, SSPs, and exchanges to auction the impression and find the right bid as per the floor price and targeting options.
Step 4. The winning advertiser is chosen, and the ad server is directed to show a video ad.
The ad server fetches the video, places it on an ad unit, and calls it an impression.
For faster delivery, ad servers sometimes take the help of CDN (content delivery network) for faster delivery of videos. Hence the speed of video ad delivery depends on the performance of ad servers.
VI. Best Practices: Tips to Succeed at Video Advertising
If not used wisely, video ads are very likely to disrupt the user experience. Here are some tips for publishers running video ads on their websites:
Always Keep the Audio Off
As per the Coalition for Better Ads, autoplay ads with audio on are marked as the most intrusive ads by users. Moreover, many browsers block such ads from appearing on their web pages (including Chrome by a method called ad filtering). If you have autoplay video ads with audio on, reconsider your strategy before advertisers and browsers start blacklisting your websites.
Maintain Minimum Viewability Standards
Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB) and Media Rating Council (MRC) definition of viewability for video advertising—a minimum of 50% of the ad is in view for a minimum of two continuous seconds. If your video ad falls into this criteria, only then you will get the advertiser’s money.
Page Load Time
Video files are bulkier than a banner, hence adding to the page load time. We already know 40% of users leave websites that take more than 3 seconds time to load, and 47% expect a website to load in 2 seconds or less. These are tough numbers to achieve, with ad monetization as your primary source of money, publishers need a better solution.
In such a case, lazy loading ads help. With lazy loading, the content of the page is allowed to load first, and heavy ads appear after a certain user engagement (like >30% page scroll). Going back to the Forbes example, video ads only appear when a user scrolls down a little. This ensures appropriate load time and impressions from users.
Try Video Header Bidding
The rest of the process remains the same as just the auction method changes in the case of video header bidding. Basically, a header auction is designed to maximize demand while keeping auction time under control. Using this methodology with video ads, publishers can save time during the auction and use it for timely video ad delivery.
Don’t Overwhelm Users
Too many ads are never good. It decreases the viewability score as users are unable to focus on content or ads, adds to page load time, and, worst of all, leads to adblocker installation. It is recommended to start with layout optimization to understand the potential of your website. Then put ad units carefully based on time spent by users on different parts of your page.
Setup an Ad Ops Team
With video ads, there would be complications related to page load time, the use of proper placements, and the requirement to understand the technology and serving process. All this, in return, will get a better revenue stream. Having an ad ops team taking care of ad monetization will make your efforts more lucrative. It is also advised to consider getting external help with ad operations, this should help with streamlining the process and bring new ideas to the table.
Consider Creating Video Content
Ads in video format complement video content. If you are looking for means to improve audience engagement and time on-site, video content is just the thing you need. In 2020, 86% of users want to see more video content from brands. Investing in video content should not only help you with brand recognition but also with better video ad monetization.
In case you wish to improve your video ad revenue, then give us – AdPushup – a try. We offer:
- Multi-Format Ads: Meaning if video doesn’t win the impression, then a banner or native can take place to avoid loss of revenue
- Top Video Demand Partners: offering you quality video ads for your users and good revenue for your business
Also Check: The Top 15 Video Ad Networks for Publishers (2023 Update)
VII. How Publishers can Transition From All-Display to Video Advertisement
Making the switch from display ads to video ads is a delicate task. Publishers need to make sure they have all the resources they need to make that process a successful one. Some of the best paths to success include:
- Turn static images into video and slideshows
- Establish inventory specifications that maximize user engagement.
- Use analytics to constantly improve ad effectiveness.
- Optimize ads to not rely on audio
- Start building your own content environment.
- Implement the Right Video Monetization Solution
(Also, refer to our advertisement documentation for more detailed information.)
VIII. Publishing Video Ads on Your Website
There are several ways to monetize video content. But, the most effective strategy is through serving ads in video format. Publishing video ads might sound like a straightforward task, but it isn’t. Well, our job today is to make the process as simple as possible for you.
Sign up for Relevant Video Ad Networks
Buy a Subscription for the Right Video Player
Set up Your Website for Video Ad Display
Select Videos to Start Displaying Ads In
Monitor Your Performance
(Also, refer to our ads publication guide for more detailed information.)
IX. How to Choose the Best Video Player for Monetization
Video players bridge the gap between the user and the ad. Some ads, like in-stream, cannot be served without a video player, and the user cannot view them without it. Furthermore, they come with additional features such as providing insights and integration with different ad networks.
Here’s how publishers can choose the best video player for them:
- Choose a video player that can support Google IMA SDK Integration.
- Choose a VAST/VPAID compliant player.
- Opt for video players that is customizable in nature with proper documentation available for tweaking the settings
- Opt for a video player that offers adoption and implementation of any ad format should be the ideal choice.
If you’re still looking for a suitable video player but cannot decide among all the available options, here’s an unbiased review of top video players for monetization.
X. How to Run Video Ads in Google Ad Manager (GAM)
Understanding the process of running ads in Google Ad Manager can get tricky in the beginning, and publishers may face technical difficulties. But the growth that video advertising will bring to your revenue is worth the effort.
In case doing this on your own is too difficult, here’s the process of implementing video ads in Google Ad Manager is a 5-step process:
- Create Ad Units
- Video Ad Tag Generation
- Create Video Line Items
- Add Creatives to Line Items
- Create Reports
XII. What’s Your Strategy for Video Ads?
As you can see, video advertisement has already massively benefited many businesses. It’s unlikely to go anywhere, so you might as well start reaping the advantages it can provide.
If you’re ready to try your hand at video advertising and see how it speeds up your ad revenue goals, then why not book a complimentary demo call with us? We’re so excited to get your feedback on the features that we spent months developing.
AdPushup leverages programmatic advertising and advanced ad technology to maximize your yield on web inventory with the new video ad units. Get started with us here.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Video ads are short videos containing a brand’s message to its users. Programmatic advertising made it possible for publishers to target, manage, and scale video advertising strategy just like their display ads.
– Keep the audio off
– Reduce page loading time
– Try video header bidding
– Don’t overwhelm users
– Set up an ad ops team
– Consider creating video content
– Maintain minimum viewability standards
Here’s how publishers can choose the best video player for them:
– Choose a video player that supports Google IMA SDK Integration.
– Choose a VAST/VPAID compliant player.
– Opt for video players that are customizable in nature
– Opt for a video player that offers the adoption of different ad formats
Video advertising allows you to engage with audiences that ignore banner ads or text. A lot of marketers are increasing ad revenue by investing in video ads. If you overlook this trend, you’ll face a competitive disadvantage.
– Instream Video Ads
– Outstream Video Ads
– Interactive Video Ads
– Pre-roll Video Ads
– Mid-roll Video Ads
– Post-roll Video Ads
– Overlay Ads
– Non-Overlay Ads

Shubham is a digital marketer with rich experience working in the advertisement technology industry. He has vast experience in the programmatic industry, driving business strategy and scaling functions including but not limited to growth and marketing, Operations, process optimization, and Sales.